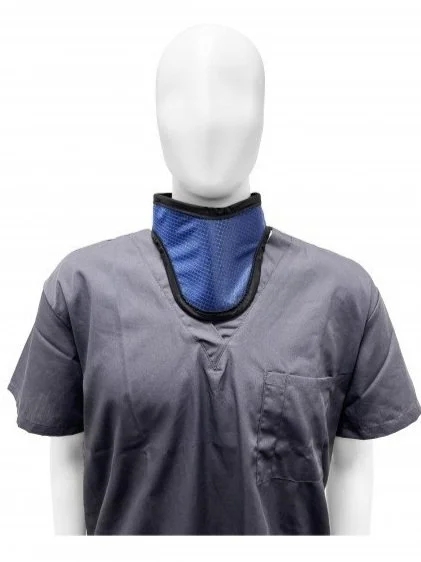
What Is a Thyroid Collar?
Thyroid collars play a critical role in maintaining safety during medical procedures involving radiation. Designed specifically to protect the thyroid gland, these collars are essential for radiology technicians, radiologists, surgeons, and other medical professionals working in environments where exposure to radiological imaging is routine. Understanding their purpose and proper use is key to ensuring both patient and provider safety.
Below, we’ll explore what thyroid collars are and how to use them, as well as answer common questions about their safety and hygiene.
Thyroid Collars: What Are They and Why Are They Important?
A thyroid collar, sometimes referred to as a thyroid shield, is a protective garment made from lead or lead-equivalent materials. It is designed to shield the thyroid gland—a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck—from exposure to ionizing radiation and scatter radiation during medical procedures such as X-rays, CT scans, and fluoroscopy.
Why protect the thyroid?
The thyroid is highly sensitive to radiation. Overexposure can increase the risk of developing thyroid-related conditions, including cancer. By blocking radiation in the area around the neck, the thyroid collar minimizes the risk of radiation induced cancer and ensures compliance with radiation safety standards in medical settings.
How Is a Thyroid Collar Used?
Thyroid collars are worn around the neck, typically secured with Velcro straps or adjustable fasteners for a snug but comfortable fit. They are most commonly used in combination with lead aprons to provide full-body protection during radiological procedures.
For radiology professionals and surgeons, thyroid collars are a part of personal protective equipment (PPE) required when working in areas where repeat or prolonged radiation exposure is likely. For patients, thyroid collars provide an added layer of protection during diagnostic imaging, particularly for procedures involving the head, neck, or upper chest.
Key Usage Tips:
Proper Fit: Ensure the collar comfortably encases the neck without being overly tight or restricting movement.
Positioning: Place the collar high enough to protect the thyroid area but low enough to avoid impeding imaging of the head or jaw.
Pairing: Always use a thyroid collar alongside other radiation protective garments, such as lead aprons or gloves, for comprehensive protection.
Is It Safe to Wear a Thyroid Collar?
Yes, thyroid collars are safe to wear and are specifically designed to reduce radiation exposure and limit radiation doses without causing discomfort to the wearer. When properly fitted, they allow for comfortable use during medical procedures while efficiently reducing the ESD (Entrance Skin Dose) by 72.3% (0.55 mGy) and other harmful radiation from reaching the thyroid gland.
For medical professionals, wearing a thyroid collar is an essential part of adhering to radiation safety protocols, protecting both themselves and their patients. For patients undergoing procedures, healthcare providers ensure collars are used only where adequate protection is required, focusing on safety without compromising diagnostic accuracy.
How Do You Clean a Thyroid Collar?
Thyroid collars are made from materials that require regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure their longevity and user safety. Over time, protective garments can collect bacteria, germs, and bodily fluids, making proper disinfection crucial.
Steps for Cleaning a Thyroid Collar:
To ensure the cleanliness, longevity, and effectiveness of thyroid collars, healthcare providers should follow these steps for regular cleanings after each use:
Choose the Right Cleaning Products: Use Clorox Hydrogen Peroxide Wipes or Ecolab Quaternary Based Wipes. These products reduce bacteria and biofilm buildup without damaging the garment material. Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
Thoroughly Clean the Entire Surface: Wipe down the entire surface of the thyroid collar, even areas that may appear clean. Harmful micro-bacteria may not be visible, so it is essential to clean all areas to maintain hygiene and infection control.
Ensure Proper Drying: After cleaning, hang or lay the thyroid collar flat to dry in an undisturbed environment. Make sure there are no creases in the garment, as they can trap moisture and impede drying. Proper drying helps prevent the growth of bacteria and preserves the integrity of the thyroid collar.
Repeat After Each Use: To maintain essential maintenance of your thyroid collar, repeat these cleaning steps after each use. Regular cleaning is crucial in slowing down bacteria and biofilm buildup, ensuring patient safety and infection control.
Deep Cleaning & Sanitization: Bacteria and biofilm build-up will happen over time even with regular wipe-downs. Governing bodies, such as AORN, recommend quarterly cleaning and sanitization of high-touch objects. You may consider deep cleaning garments in-house. However, properly deep cleaning and sanitizing garments requires specialized tools, equipment, and knowledge. You can learn more here.
For more comprehensive instructions and insights on cleaning lead aprons, we recommend referring to the informative blog post on How to Clean Lead Aprons. By following these cleaning procedures, healthcare providers prioritize patient safety, infection control, and the longevity of thyroid collars.
Should I Wear a Thyroid Collar Someone Else Has Worn?
American Thyroid Association knows that hygiene is paramount when it comes to shared medical equipment. While most thyroid collars in medical facilities are reusable, it is critical that they are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected between uses to prevent the spread of infections to protect patients.
Before wearing a thyroid collar that has been used by someone else, verify that proper cleaning protocols have been followed. Some facilities implement advanced cleaning services, like regular X-ray garment deep cleaning & sanitization services, to ensure that all protective equipment meets stringent hygiene standards.
Where Can I Get a Comfortable Thyroid Collar?
Finding the right thyroid collar involves choosing a product that offers a balance between protection, comfort, and durability. Many medical suppliers and specialty providers offer high-quality thyroid collars made from lead-equivalent materials that are lightweight yet effective.
Key Features to Look For:
Adjustable Fit: A collar with adjustable straps ensures a secure and comfortable fit.
Lead-Equivalent Options: Lighter alternatives, such as lead-equivalent or lead-free thyroid collars, reduce strain on the wearer without compromising protection.
Durability: Look for materials that withstand frequent use and consistent cleaning.
Reputable brands known for radiation protective gear typically carry a range of thyroid collars suitable for professionals and patients alike. We offer Burlington Medical, Techno-Aide, and INFAB and will help find the right garment for your needs.
Invest in Safety and Confidence
The use of thyroid collars is essential in modern medical environments, offering an effective way to protect a delicate and radiation-sensitive gland. Whether you’re a radiology technician, radiologist, or surgeon, understanding how to use and maintain this vital piece of equipment properly ensures patient well-being and significantly reduces occupational radiation risks.
If you need a thyroid collar, we can help. We provide thyroid collars and other radiation protection equipment from reputable manufacturers. Our team will help find the right garment for your needs.