Professional Lead Garment Inspection and X-Ray Scanning Services
Visual inspections miss the invisible cracks and lead deterioration that put your staff and patients at risk. RCS provides comprehensive radiographic inspection services that detect hidden damage while reducing radiation exposure risk for your team and ensuring compliance.

Trusted by 500+ Teams
Why Annual Lead Garment X-ray Inspections Are Critical
Damaged X-ray garments expose staff to unknown radiation.
The Joint Commission and other regulations require annual inspection of all lead protective equipment to verify radiation protection integrity. Visual and tactile inspections alone cannot detect micro-cracks that compromise protection. Only radiographic inspection reveals the hidden defects that put healthcare workers at risk.
The Hidden Dangers:
- Visual and palpation checks miss internal damage
- Cracks compromise radiation protection
- Unknown damage = unknown exposure
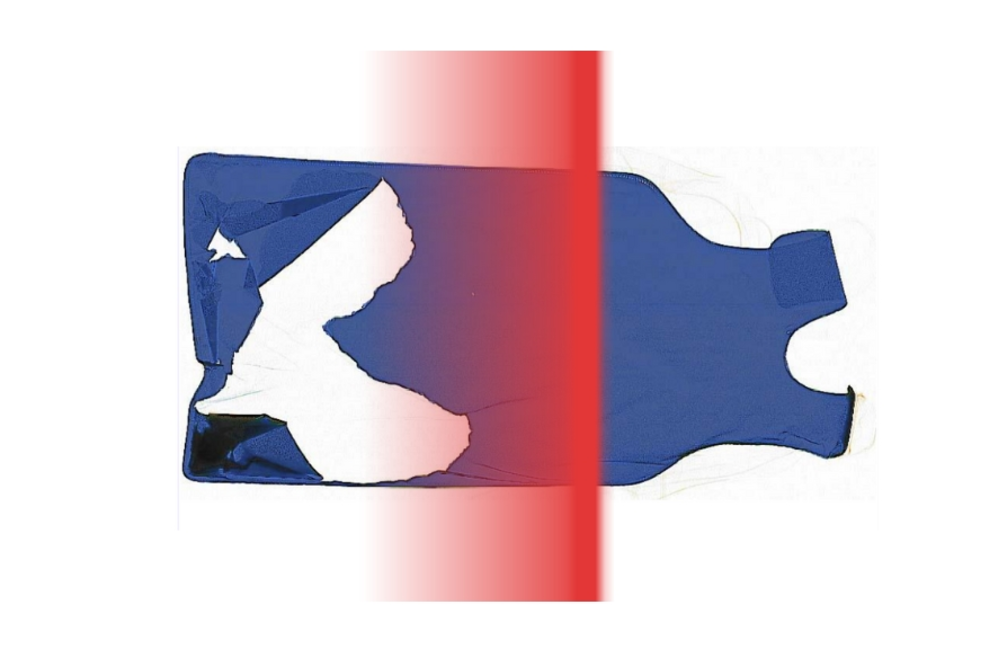
Comprehensive Radiographic Inspection
Every garment undergoes an annual radiographic examination to detect cracks and tears that are invisible to visual inspection. We assess each garment’s condition and flag those that appear damaged or may no longer meet safety standards.
Our Process Includes:
- Annual X-ray Inspection
- Three year image archive
- History accessible via QR code on garment tag & in RadComply®
When Your Garments Return:
You receive a comprehensive report, including radiographic images of each garment, stored in RadComply for audit compliance. Detected damage is clearly reported, allowing your facility to determine pass/fail status in accordance with your internal protocols. Year-over-year image comparison helps you track deterioration patterns and forecast replacement needs accurately.


Professional inspection minimizes radiation exposure risks
After garments are collected, they enter our inspection facility, where trained technicians perform a comprehensive radiographic examination. Every garment is scanned annually to detect defects. All inspection images are captured, analyzed, and archived in RadComply for a period of three years, accompanied by detailed documentation for regulatory compliance. Your team can efficiently pass/fail garments depending on your internal protocols.
- Stress-free compliance
- Less downtime, more patient care
- Radiation safety you can verify
Radiographic Scanning
Each garment scanned to reveal hidden defects.
Image Analysis
Technicians analyze scans and document findings.
Efficient Approvals
RadComply makes it easy to pass/fail garments depending on your internal protocols.
Compliance Reporting
Inspection records stored in RadComply, ready for audits.
Statistics That Matter:
13 Minutes Saved
Facilities saved on average 13 minutes per garment by using RCS services.
Reduce Unknown Exposure Risks
On average, 11% of first time customer garments have protective material damage.
1.5-2X Garment Lifespan
Garments serviced by RCS see, on average, a 1.5-2x increase in lifespan compared to garments not serviced by RCS.
100% Documented
Every garment scan is archived in RadComply with images ready for regulatory audits.
Stay safe, stay compliant, and get more life out of your lead aprons with professional inspections.
Annual radiographic inspection is more than a regulatory requirement. It’s essential protection against radiation exposure from compromised garments, and it documents your commitment to staff safety during audits and surveys. Early detection prevents exposure incidents and extends the useful life of your inventory through proactive replacement planning.
How To Get Started
Starting with RCS is simple. We assess your facility’s needs, design a service plan to match, and handle every detail. Your garments stay compliant, and your team stays focused.
Schedule Your Consultation
Connect with our team to discuss your current garment inventory, department needs, and compliance requirements.
Choose Your Service Model
Select RadOnsite for convenient on-site pickup and delivery, or RadShip for a streamlined shipping-based solution with loaner garments included.
Experience Seamless Service
RCS handles your lead garment program from end to end, while you access real-time inventory, compliance data, and X-ray scan results in RadComply.
Ready To Say Goodbye To Filthy Lead?
Lead Garment Cleaning & Care: What Every Hospital Needs to Know
Clean Those Leads
Hospital-owned lead garments require professional deep cleaning, not just surface wipes. RCS follows a proven two-step cleaning and disinfection process that meets AORN, The Joint Commission, and CDC standards to eliminate bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores.
Save Time
RCS customers save an average of 13 minutes per garment by eliminating the need for staff to perform manual X-ray scans, track inventory spreadsheets, and manage repair schedules. Our service frees your radiology techs and clinical staff to focus on patient care instead of garment management.
84% Of Lead Vest Are Contaminated
A Wayne State University study found that 84% of lead aprons tested positive for Ringworm and Staphylococcus aureus, with 12% colonized by MRSA. Contaminated protective equipment puts both healthcare workers and patients at risk of infection.
Wipes Aren’t Enough
Surface wipes alone are clinically proven ineffective for properly sanitizing lead garments. True sanitization requires a two-step process: friction-based cleaning followed by proper sanitization using bactericidal, viricidal, fungicidal, and sporicidal solutions.








